Implicit Neural Representation for Image Demosaicking
2025 Digital Signal Processing: A Review Journal
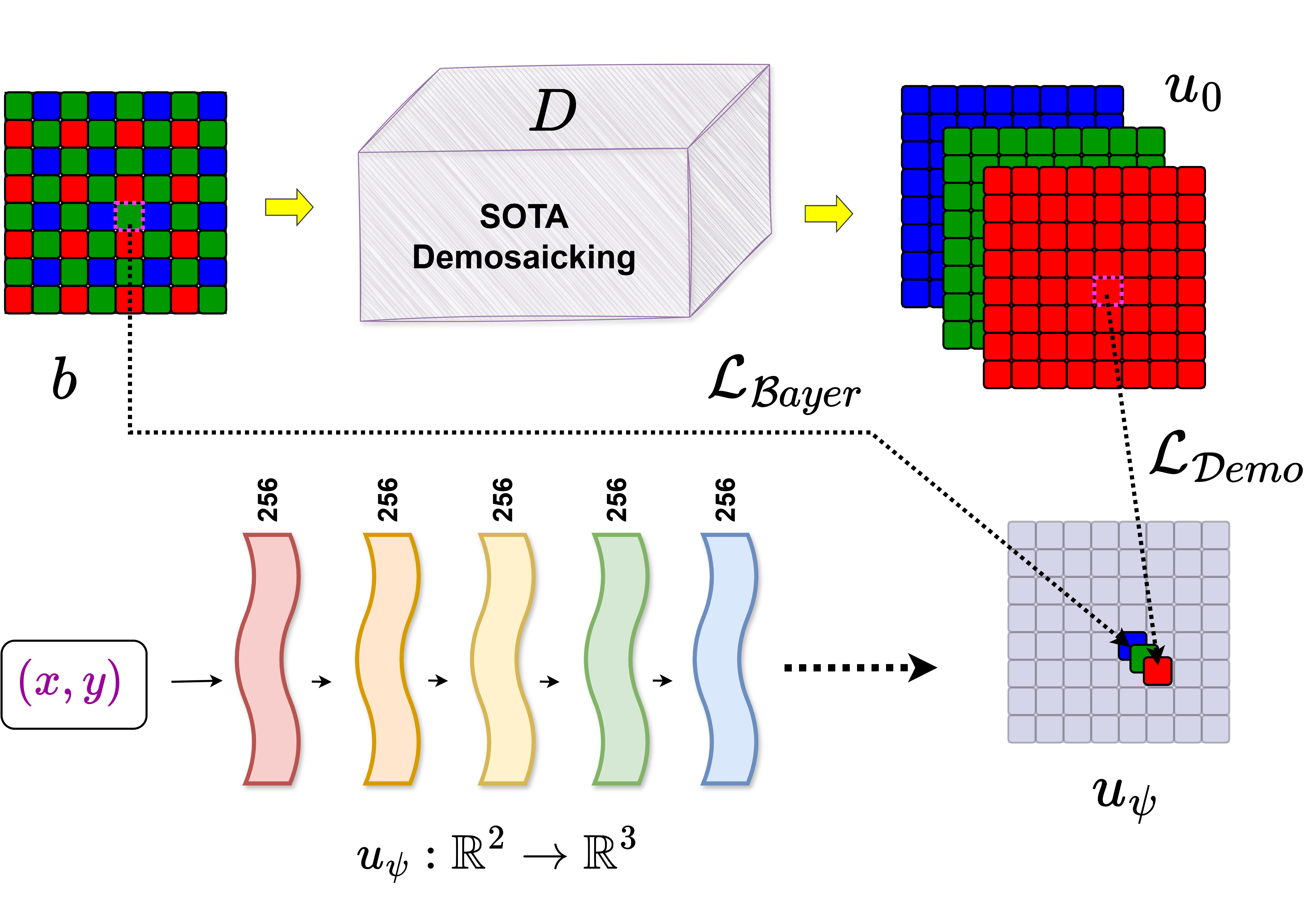
We propose a novel approach to enhance image demosaicking algorithms using implicit neural representations (INR). Our method employs a multi-layer perceptron to encode RGB images, combining original Bayer measurements with an initial estimate from existing demosaicking methods to achieve superior reconstructions. A key innovation is the integration of two loss functions: a Bayer loss for fidelity to sensor data and a complementary loss that regularizes reconstruction using interpolated data from the initial estimate. This combination, along with INR's inherent ability to capture fine details, enables high-fidelity reconstructions that incorporate information from both sources. Furthermore, we demonstrate that INR can effectively correct artifacts in state-of-the-art demosaicking methods when input data diverge from the training distribution, such as in cases of noise or blur. This adaptability highlights the transformative potential of INR-based demosaicking, offering a robust solution to this challenging problem.